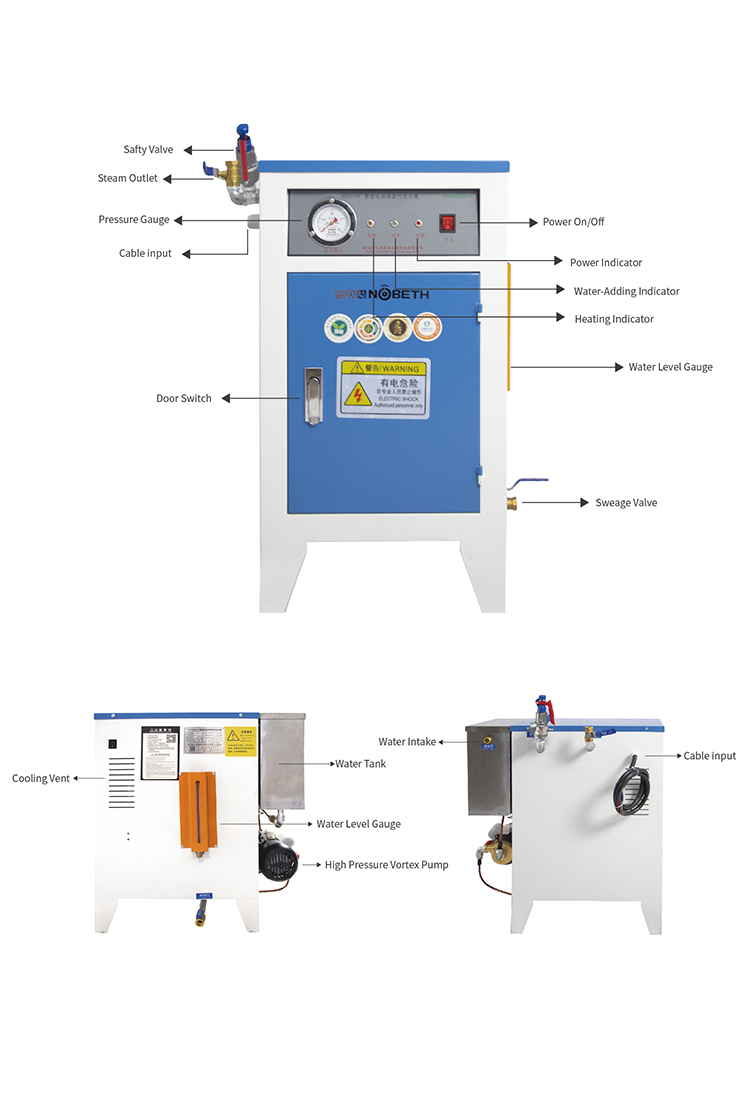
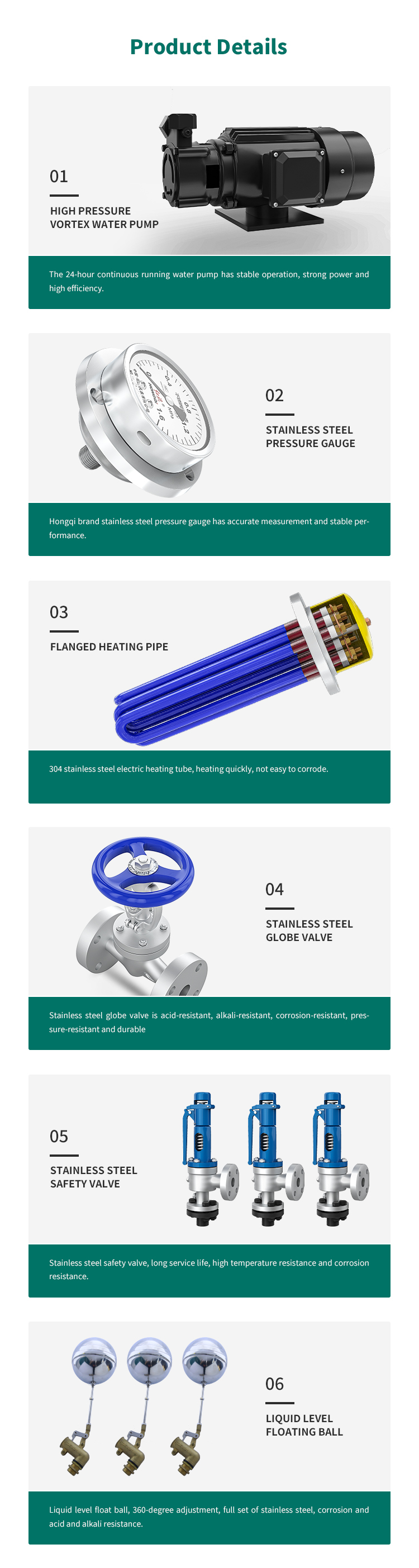
3kw Electric steam boiler for ironing
According to EN285, the air detection test can be carried out to verify whether the air is successfully excluded.
There are two ways to remove air:
Downward (gravity) discharge method – Because steam is lighter than air, if steam is injected from the top of the sterilizer, the air will accumulate at the bottom of the sterilization chamber where it can be discharged.
The forced vacuum discharge method is to use a vacuum pump to remove the air in the sterilization chamber before injecting steam. This process can be repeated several times to remove as much air as possible.
If the load is packaged in a porous material or the structure of the device may allow air to accumulate (for example, devices with narrow lumens such as straws, cannulaes), it is very important to evacuate the sterilization chamber, and the exhaust air should be handled carefully , as it may contain dangerous substances to be killed.
The purge gas should be filtered or sufficiently heated before being vented to the atmosphere. Exhaust air that is not treated has been associated with increased rates of nosocomial disease in hospitals (nosocomial diseases are those that occur in a hospital setting).
4. Steam injection means that after steam is injected into the sterilizer under the required pressure, it takes a period of time to make the entire sterilization chamber and the load reach the sterilization temperature. This period of time is called “equilibrium time”.
After reaching the sterilizing temperature, the entire sterilizing chamber is kept in a sterilizing temperature zone for a period of time according to this temperature, which is called the holding time. Different sterilization temperatures correspond to different minimum holding times.
5. The cooling and elimination of steam is that after the holding time, the steam is condensed and discharged from the sterilization chamber through the steam trap. Sterile water can be sprayed into the sterilization chamber or compressed air can be used to accelerate cooling. It may be necessary to cool the load to room temperature.
6. Drying is to vacuumize the sterilization chamber to evaporate the water remaining on the surface of the load. Alternatively, a cooling fan or compressed air can be used to dry the load.
Products categories
-

E-mail
-
Phone
-

WhatsApp
-
Top