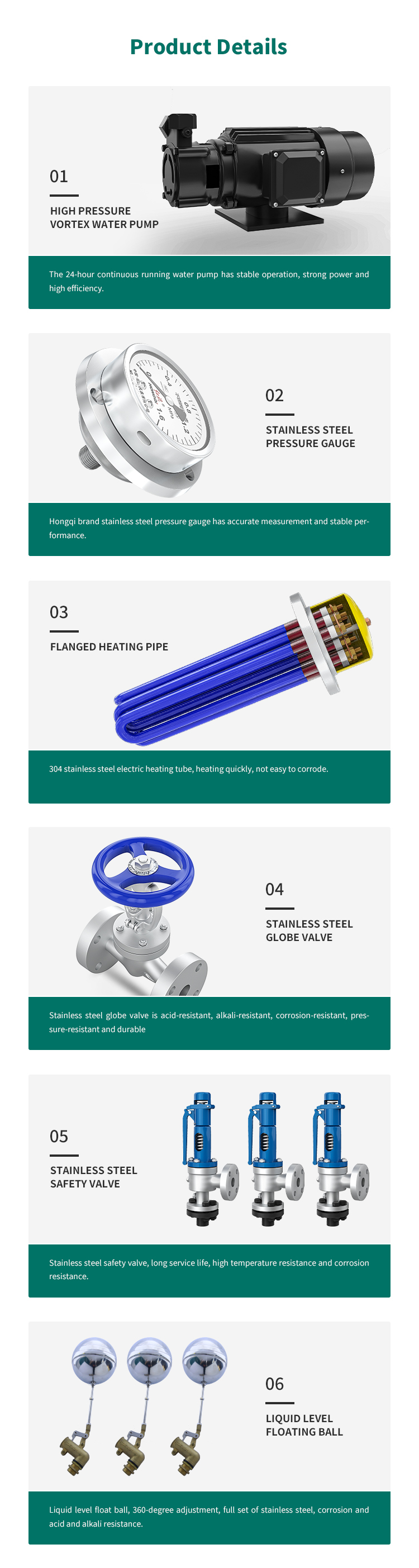
720KW Customized Steam Generator
According to the high calorific value, the loss items in the heat loss method are:
1. Dry smoke heat loss.
2. Heat loss due to the formation of moisture from hydrogen in the fuel.
3. Heat loss due to moisture in the fuel.
4. Loss of heat due to moisture in the air.
5. Flue gas sensible heat loss.
6. Incomplete combustion heat loss.
7. Superposition and conduction heat loss.
8. Pipeline heat loss.
The difference between the upper calorific value and the lower calorific value depends on whether the latent heat of vaporization of water vapor (formed by dehydration and hydrogen combustion) is released. That is, the thermal efficiency of steam generators based on high-heat stars is somewhat lower. It is generally stipulated that fuels with low calorific value are selected, because the water vapor in the flue gas does not condense and does not release latent heat of vaporization during actual operation. However, when calculating the exhaust loss, the water vapor in the flue gas does not include its latent heat of vaporization.
Products categories
-

E-mail
-
Phone
-

WhatsApp
-
Top