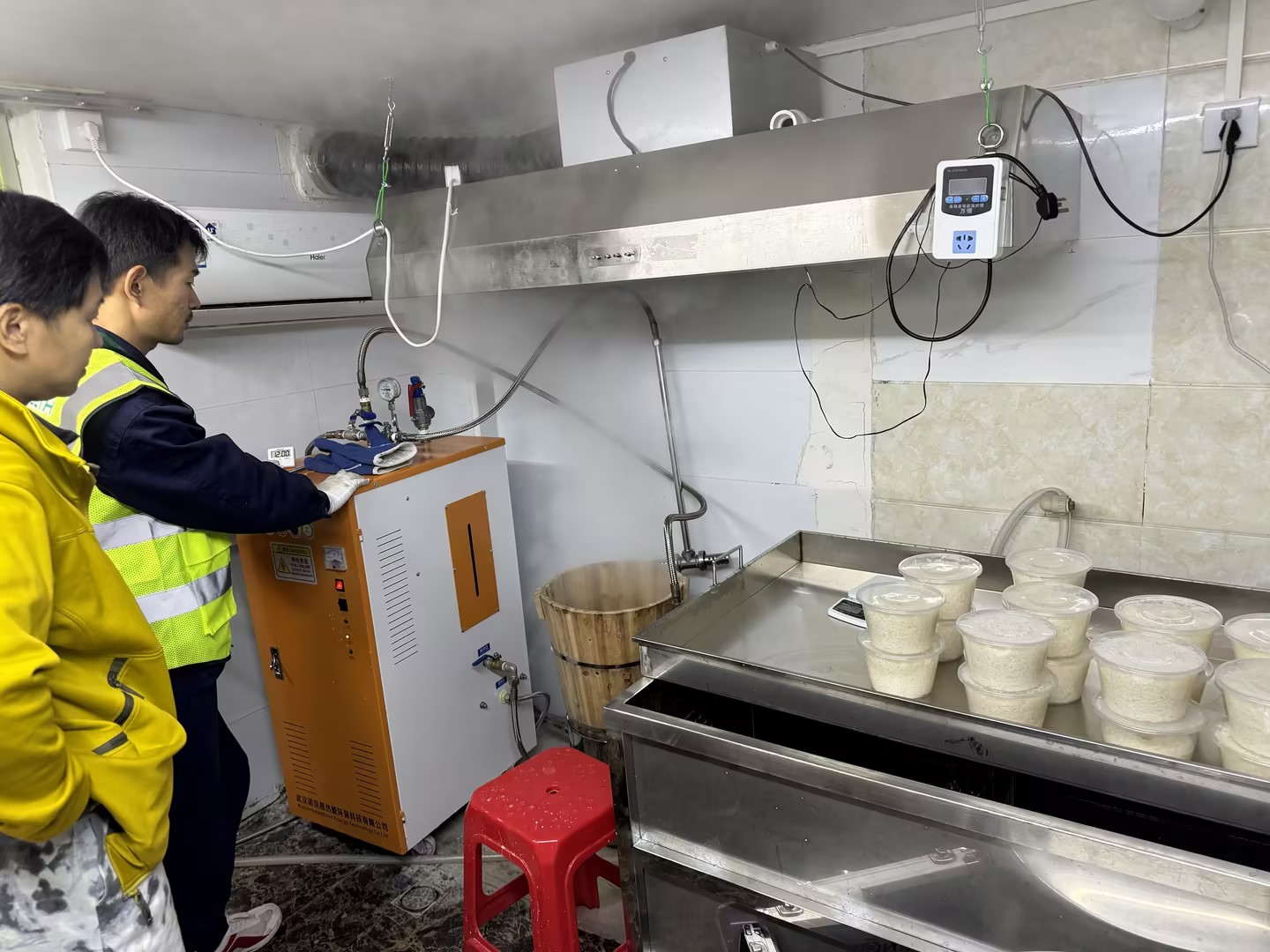
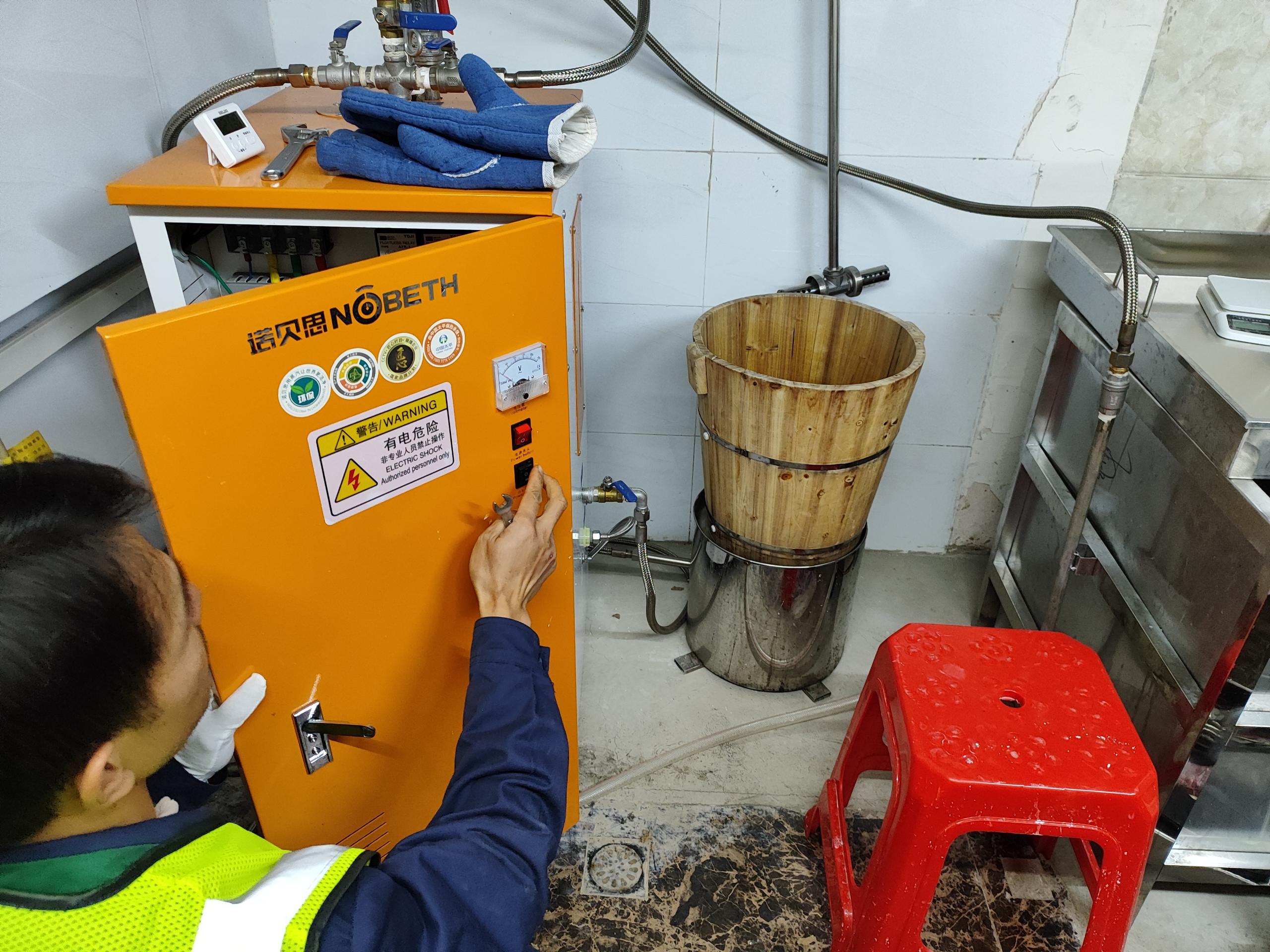
Any product will have some parameters. The main parameter indicators of steam boilers mainly include steam generator production capacity, steam pressure, steam temperature, water supply and drainage temperature, etc. The main parameter indicators of different models and types of steam boilers will also be different. Next, Nobeth takes everyone to understand the basic parameters of steam boilers.
Evaporation capacity: The amount of steam generated by the boiler per hour is called evaporation capacity t/h, represented by the symbol D. There are three types of boiler evaporation capacity: rated evaporation capacity, maximum evaporation capacity and economic evaporation capacity.
Rated evaporation capacity: The value marked on the boiler product nameplate indicates the evaporation capacity generated per hour by the boiler using the originally designed fuel type and operating continuously for a long time at the original designed working pressure and temperature.
Maximum evaporation capacity: Indicates the maximum amount of steam generated by the boiler per hour in actual operation. At this time, the efficiency of the boiler will be reduced, so long-term operation at the maximum evaporation capacity should be avoided.
Economic evaporation capacity: When the boiler is in continuous operation, the evaporation capacity when the efficiency reaches the highest level is called economic evaporation capacity, which is generally about 80% of the maximum evaporation capacity. Pressure: The unit of pressure in the International System of Units is Newton per square meter (N/cmi’), represented by the symbol pa, which is called “Pascal”, or “Pa” for short.
Definition: The pressure formed by a force of 1N evenly distributed over an area of 1cm2.
1 Newton is equivalent to the weight of 0.102kg and 0.204 pounds, and 1kg is equal to 9.8 Newtons.
The commonly used pressure unit on boilers is megapascal (Mpa), which means million pascals, 1Mpa=1000kpa=1000000pa
In engineering, the atmospheric pressure of a project is often written approximately as 0.098Mpa;
One standard atmospheric pressure is approximately written as 0.1Mpa
Absolute pressure and gauge pressure: The medium pressure higher than the atmospheric pressure is called positive pressure, and the medium pressure lower than the atmospheric pressure is called negative pressure. Pressure is divided into absolute pressure and gauge pressure according to different pressure standards. Absolute pressure refers to the pressure calculated from the starting point when there is no pressure at all in the container, recorded as P; while gauge pressure refers to the pressure calculated from the atmospheric pressure as the starting point, recorded as Pb. So gauge pressure refers to pressure above or below atmospheric pressure. The above pressure relationship is: absolute pressure Pj = atmospheric pressure Pa + gauge pressure Pb.
Temperature: It is a physical quantity that expresses the hot and cold temperatures of an object. From a microscopic perspective, it is a quantity that describes the intensity of thermal motion of the molecules of an object. Specific heat of an object: Specific heat refers to the heat absorbed (or released) when the temperature of a unit mass of a substance increases (or decreases) by 1C.
Water steam: A boiler is a device that generates water steam. Under constant pressure conditions, water is heated in the boiler to generate water steam, which generally goes through the following three stages.
Water heating stage: Water fed into the boiler at a certain temperature is heated at a constant pressure in the boiler. When the temperature rises to a certain value, the water begins to boil. The temperature when the water boils is called the saturation temperature, and its corresponding pressure is called the saturation temperature. saturation pressure. There is a one-to-one correspondence between saturation temperature and saturation pressure, that is, one saturation temperature corresponds to one saturation pressure. The higher the saturation temperature, the higher the corresponding saturation pressure.
Generation of saturated steam: When water is heated to saturation temperature, if heating at constant pressure continues, the saturated water will continue to generate saturated steam. The amount of steam will increase and the amount of water will decrease until it is completely vaporized. During this entire process, its temperature remains unchanged.
Latent heat of vaporization: The heat required to heat 1kg of saturated water under constant pressure until it is completely vaporized into saturated steam at the same temperature, or the heat released by condensing this saturated steam into saturated water at the same temperature, is called the latent heat of vaporization. The latent heat of vaporization changes with the change of saturation pressure. The higher the saturation pressure, the smaller the latent heat of vaporization.
Generation of superheated steam: When dry saturated steam is continued to be heated at a constant pressure, the steam temperature rises and exceeds the saturation temperature. Such steam is called superheated steam.
The above are some basic parameters and terminology of steam boilers for your reference when selecting products.
Post time: Nov-24-2023