A:
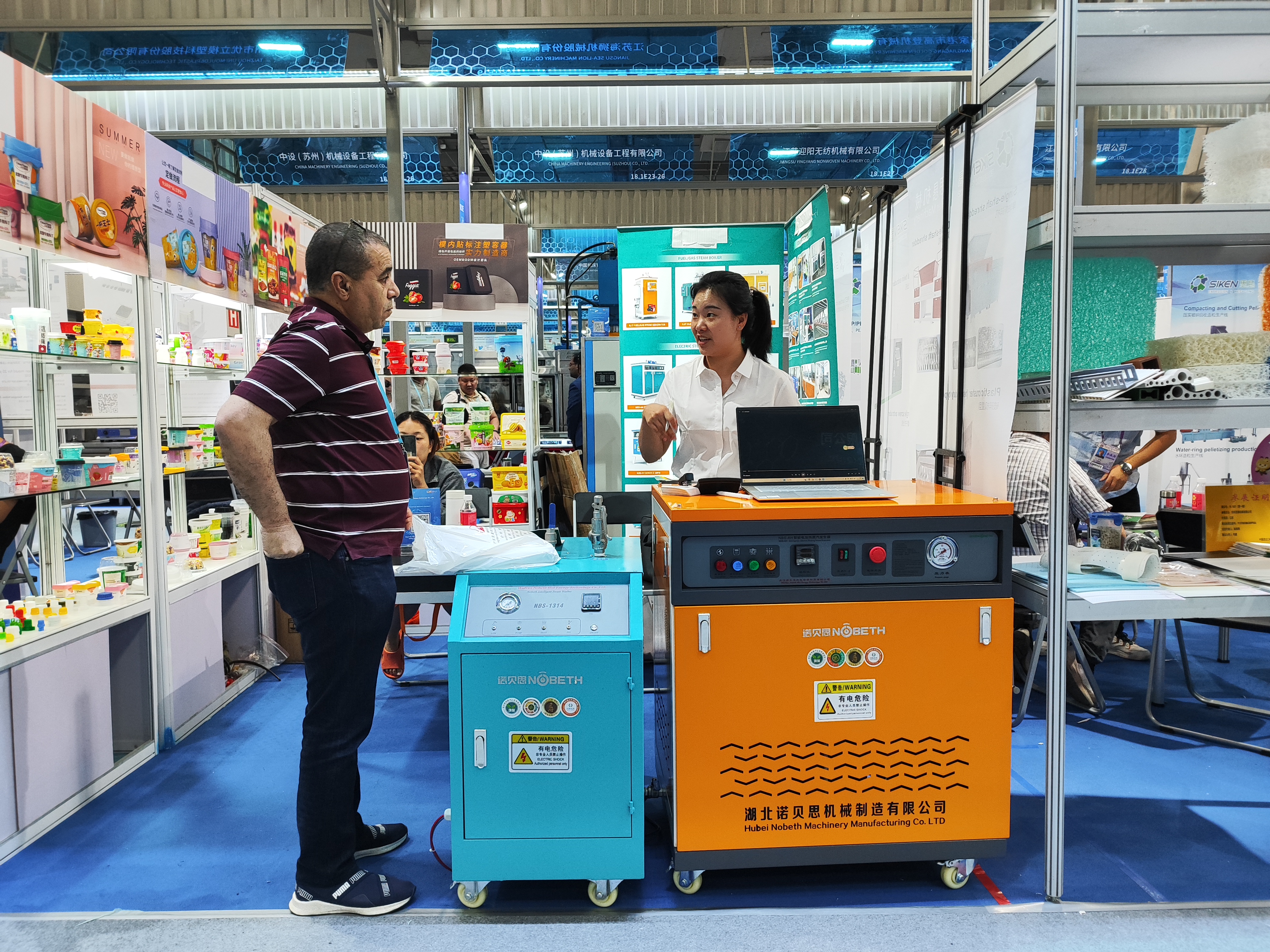
Tap water: Tap water refers to water that is produced after purification and disinfection by tap water treatment plants and meets corresponding standards for people’s living and production use. The tap water hardness standard is: national standard 450mg/L.
Softened water: refers to water in which the hardness (mainly calcium and magnesium ions in the water) has been removed or reduced to a certain extent. During the process of softening water, only the hardness decreases, but the total salt content remains unchanged.
Demineralized water: refers to water in which salts (mainly strong electrolytes dissolved in water) have been removed or reduced to a certain extent. Its conductivity is generally 1.0~10.0μS/cm, resistivity (25℃)(0.1~1.0)×106Ω˙cm, and salt content is 1~5mg/L.
Pure water: refers to water in which strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes (such as SiO2, CO2, etc.) are removed or reduced to a certain level. Its electrical conductivity is generally: 1.0~0.1μS/cm, electrical conductivity (1.01.0~10.0)×106Ω˙cm. Salt content is <1mg/L.
Ultrapure water: refers to water in which the conductive medium in the water is almost completely removed, and at the same time, non-dissociated gases, colloids and organic substances (including bacteria, etc.) are also removed to a very low level. Its conductivity is generally 0.1~0.055μS/cm, resistivity (25℃)﹥10×106Ω˙cm, and salt content﹤0.1 mg/L. The (theoretical) conductivity of ideal pure water is 0.05μS/cm, and the resistivity (25℃) is 18.3×106Ω˙cm.
Post time: Nov-01-2023